源码分析
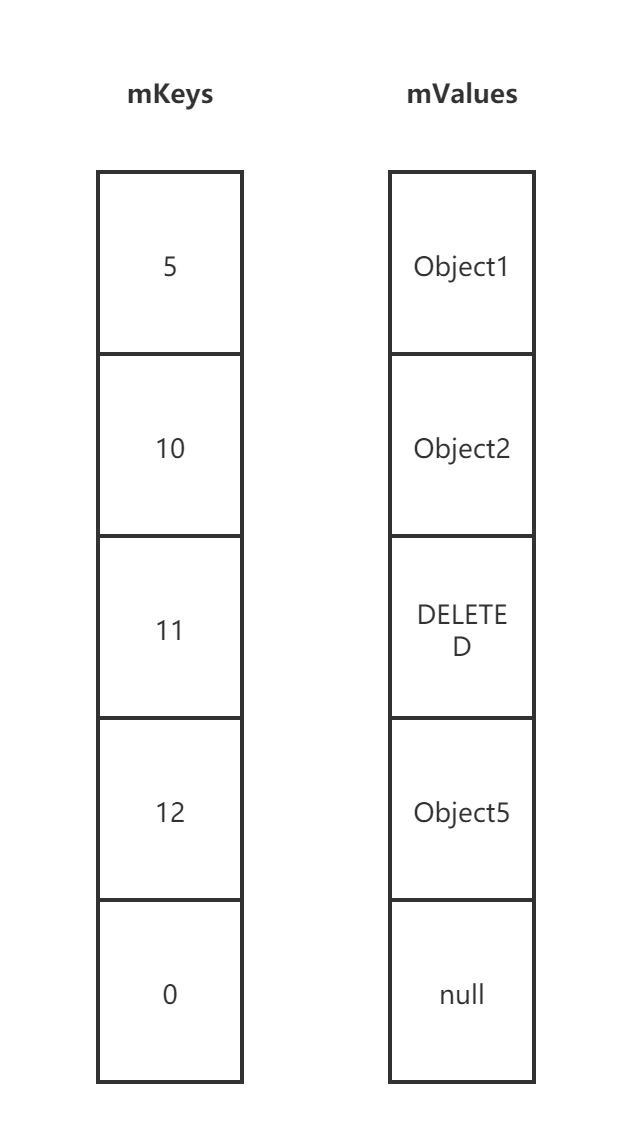
构造方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public SparseArray() {
// 默认容量为 initialCapacity
this(10);
}
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
// 当 initialCapacity 为偶数时创建大小为 initialCapacity+1 大小的数组,每个值都为 null
// 当 initialCapacity 为奇数时创建大小为 initialCapacity 大小的数组,每个值都为 null
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
// 创建大小为 mValues.lenght 的数组,每个值都为 0
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}
put 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public void put(int key, E value) {
// 通过 二分查找 找到 key,如果 key 已经存在返回 key 的位置,如果 key 不存在返回应该插入的位置取反的值,这个值是一个负数
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
// 如果找到对应的值直接替换
mValues[i] = value;
} else {
i = ~i;
// 如果应该插入的位置,存放的是已经删除的标值位,则直接插入
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
//mGarbage 表示是否含有 Value 为 DELETED 的数据,如果通过 deleted 或者 removeAt 方法清除数据 mGarbage 就会置为 true
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
// gc 方法会删除 value 为 DELETED 的数据,并把有效数据移动到数组前面部分
gc();
// GC 后重新获取插入位置
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
// 如果 mSize < mKeys.length 插入到源数组,如果 mSize= mKeys.length 新建一个数组
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}
SparseArray.gc()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
// 将有效数据,向前移动,剔除 value 为 DELETED 的数据
private void gc() {
int n = mSize;
int o = 0;
int[] keys = mKeys;
Object[] values = mValues;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Object val = values[i];
if (val != DELETED) {
if (i != o) {
keys[o] = keys[i];
values[o] = val;
values[i] = null;
}
o++;
}
}
mGarbage = false;
mSize = o;
}
GrowingArrayUtils.insert 插入,扩容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public static <T> T[] insert(T[] array, int currentSize, int index, T element) {
assert currentSize <= array.length;
if (currentSize + 1 <= array.length) { // 当前数组长度够用
System.arraycopy(array, index, array, index + 1, currentSize - index);
array[index] = element;
return array;
}
//当前数组长度不够用,需要扩容
// ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedArray 方法,如果传入大小为偶数会+1 变为奇数
// 扩容大小:如果原来大小 小于等于 4 扩容为 9,如果大于4 扩容为原来大小的两倍+1
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] newArray = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedArray((Class<T>)array.getClass().getComponentType(),
growSize(currentSize));
// copy 前半部分
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, index);
// 插入数值
newArray[index] = element;
// copy 后半部分
System.arraycopy(array, index, newArray, index + 1, array.length - index);
// 返回新数组
return newArray;
}
public static int growSize(int currentSize) {
return currentSize <= 4 ? 8 : currentSize * 2;
}
get 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
//通过二分查找,找到key 所在位置
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {
// 如果没有找到 返回 默认值
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
// 如果找到返回对应的 value
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}
delete 和 remove
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public void remove(int key) {
delete(key);
}
public void delete(int key) {
// 二分查找对应的位置
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
// 如果存在,将其值置为 DELETED
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
mValues[i] = DELETED;
// 是否含有垃圾数据,置为 true,用于gc() 方法判断
mGarbage = true;
}
}
}
// 逻辑和 delete 类似
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (index >= mSize && UtilConfig.sThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
if (mValues[index] != DELETED) {
mValues[index] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
####
总结
- 数组大小会补充为奇数
- 默认容量为 10 ,经过补充会变为 11
- 底层数据结构为两个相同大小的数组
- key 和 value,保存在两个数组下相同角标的位置上
- key 数组按照 key 大小顺序排列
- 查找 key 的方式,是二分查找,时间复杂度为 O(log2n)
- 删除元素并不会从数组中直接移除,而是将其 value 值,置为 DELETED
- 扩容大小:如果原来大小 小于等于 4 扩容为 9,如果大于4 扩容为原来大小的两倍+1
SparseArray 相对于 HashMap 有什么优缺点
优点:
- 避免了对key的自动装箱(int转为Integer类型)
- 使用二分查找通常情况下比 HashMap hashcode 求数组下标+遍历链表 的方式效率更高
- 删除方法更简单,只是简单的将 value 标记为删除 DELETED
缺点:
- 由于 SparseArray 添加、查找、删除数据都需要先进行一次二分查找,所以在数据量大的情况下性能并不明显