App 启动流程
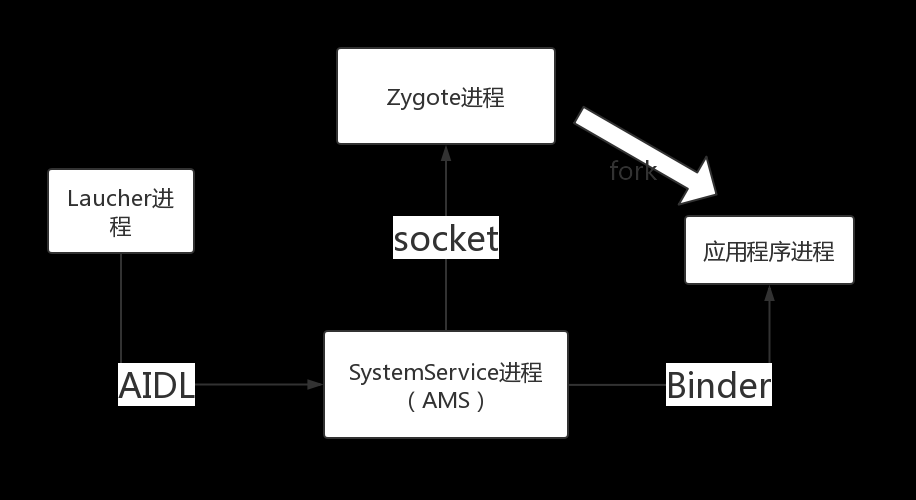
前面流程和 启动 Activity 相同直到方法
ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivity()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
void startSpecificActivity(ActivityRecord r, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) {
// Is this activity's application already running?
final WindowProcessController wpc =
mService.getProcessController(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid);
boolean knownToBeDead = false;
// 如果目标进程已经开始,并且主线程已经开启 调用 realStartActivityLocked 启动 activity
if (wpc != null && wpc.hasThread()) {
try {
realStartActivityLocked(r, wpc, andResume, checkConfig);
return;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting activity "
+ r.intent.getComponent().flattenToShortString(), e);
}
knownToBeDead = true;
}
r.notifyUnknownVisibilityLaunchedForKeyguardTransition();
final boolean isTop = andResume && r.isTopRunningActivity();
// 开启进程
mService.startProcessAsync(r, knownToBeDead, isTop, isTop ? "top-activity" : "activity");
}
检查目标进程是否存在,如果不存在调用 ActivityTaskManagerService.startProcessAsync() 启动进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
void startProcessAsync(ActivityRecord activity, boolean knownToBeDead, boolean isTop,
String hostingType) {
try {
if (Trace.isTagEnabled(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER)) {
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "dispatchingStartProcess:"
+ activity.processName);
}
// Post message to start process to avoid possible deadlock of calling into AMS with the
// ATMS lock held.
final Message m = PooledLambda.obtainMessage(ActivityManagerInternal::startProcess,
mAmInternal, activity.processName, activity.info.applicationInfo, knownToBeDead,
isTop, hostingType, activity.intent.getComponent());
mH.sendMessage(m);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
}
}
startProcessAsync 方法发送了一个 PooledLambda 生成的 message ,这个 message 最终会执行到 ActivityManagerInternal::startProcess 方法上。ActivityManagerInternal 是一个抽象,他的实现在 ActivityManagerService.LocalService ,因此最终调用到
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
@Override
public void startProcess(String processName, ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead,
boolean isTop, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName) {
try {
if (Trace.isTagEnabled(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER)) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "startProcess:"
+ processName);
}
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
// If the process is known as top app, set a hint so when the process is
// started, the top priority can be applied immediately to avoid cpu being
// preempted by other processes before attaching the process of top app.
startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, 0 /* intentFlags */,
new HostingRecord(hostingType, hostingName, isTop),
ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_LATENCY_SENSITIVE, false /* allowWhileBooting */,
false /* isolated */, true /* keepIfLarge */);
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
@GuardedBy("this")
final ProcessRecord ActivityManagerService.startProcessLocked(String processName,
ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
HostingRecord hostingRecord, int zygotePolicyFlags, boolean allowWhileBooting,
boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge) {
return mProcessList.startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags,
hostingRecord, zygotePolicyFlags, allowWhileBooting, isolated, 0 /* isolatedUid */,
keepIfLarge, null /* ABI override */, null /* entryPoint */,
null /* entryPointArgs */, null /* crashHandler */);
}
@GuardedBy("mService")
final ProcessRecord ProcessList.startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,
boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, HostingRecord hostingRecord,
int zygotePolicyFlags, boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid,
boolean keepIfLarge, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs,
Runnable crashHandler) {
final boolean success =
startProcessLocked(app, hostingRecord, zygotePolicyFlags, abiOverride);
return success ? app : null;
}
总结:
调用 startProcessLocked 开启进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
@GuardedBy("mService")
boolean startProcessLocked(HostingRecord hostingRecord, String entryPoint, ProcessRecord app,
int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int zygotePolicyFlags, int mountExternal,
String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith,
long startTime) {
final Process.ProcessStartResult startResult;
if (hostingRecord.usesWebviewZygote()) {
startResult = startWebView(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName, app.mDisabledCompatChanges,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
} else if (hostingRecord.usesAppZygote()) {
final AppZygote appZygote = createAppZygoteForProcessIfNeeded(app);
// We can't isolate app data and storage data as parent zygote already did that.
startResult = appZygote.getProcess().start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, app.info.packageName,
/*zygotePolicyFlags=*/ ZYGOTE_POLICY_FLAG_EMPTY, isTopApp,
app.mDisabledCompatChanges, pkgDataInfoMap, whitelistedAppDataInfoMap,
false, false,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
} else {
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, app.info.packageName, zygotePolicyFlags,
isTopApp, app.mDisabledCompatChanges, pkgDataInfoMap,
whitelistedAppDataInfoMap, bindMountAppsData, bindMountAppStorageDirs,
new String[]{PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
}
}
总结 : 最终会调用 Procee.start
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
public static ProcessStartResult Process.start(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, @Nullable int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags,
int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
@Nullable String packageName,
int zygotePolicyFlags,
boolean isTopApp,
@Nullable long[] disabledCompatChanges,
@Nullable Map<String, Pair<String, Long>>
pkgDataInfoMap,
@Nullable Map<String, Pair<String, Long>>
whitelistedDataInfoMap,
boolean bindMountAppsData,
boolean bindMountAppStorageDirs,
@Nullable String[] zygoteArgs) {
return ZYGOTE_PROCESS.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, packageName,
zygotePolicyFlags, isTopApp, disabledCompatChanges,
pkgDataInfoMap, whitelistedDataInfoMap, bindMountAppsData,
bindMountAppStorageDirs, zygoteArgs);
}
总结:
ZYGOTE_PROCESS 是 ZygoteProcess 类的一个静态单例
ZygoteProcess.start 会调用 ZygoteProcess.startViaZygote
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(@NonNull final String processClass,
@Nullable final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
@Nullable final int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
@Nullable String seInfo,
@NonNull String abi,
@Nullable String instructionSet,
@Nullable String appDataDir,
@Nullable String invokeWith,
boolean startChildZygote,
@Nullable String packageName,
int zygotePolicyFlags,
boolean isTopApp,
@Nullable long[] disabledCompatChanges,
@Nullable Map<String, Pair<String, Long>>
pkgDataInfoMap,
@Nullable Map<String, Pair<String, Long>>
whitelistedDataInfoMap,
boolean bindMountAppsData,
boolean bindMountAppStorageDirs,
@Nullable String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi),
zygotePolicyFlags,
argsForZygote);
}
总结:这个方法设置了一些启动参数,最终调用 ZygoteProcess .openZygoteSocketIfNeeded 打开一个 socket 通道,然后调用 ZygoteProcess.zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult 再调用 ZygoteProcess.attemptZygoteSendArgsAndGetResult 发送数据启动进程
接下来我们看 socket 的服务端 ZygoteInit
首先是 ZygoteInit 的 main 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
public static void ZygoteInit.main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = null;
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
Runnable caller;
try {
// Store now for StatsLogging later.
final long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
final boolean isRuntimeRestarted = "1".equals(
SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"));
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.preForkInit();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String zygoteSocketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
zygoteSocketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
final boolean isPrimaryZygote = zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.PRIMARY_SOCKET_NAME);
if (!isRuntimeRestarted) {
if (isPrimaryZygote) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
startTime);
} else if (zygoteSocketName.equals(Zygote.SECONDARY_SOCKET_NAME)) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SECONDARY_ZYGOTE_INIT_START,
startTime);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
}
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
Zygote.initNativeState(isPrimaryZygote);
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer(isPrimaryZygote);
if (startSystemServer) {
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
if (zygoteServer != null) {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
总结: 首先会创建一个 ZygoteServer 服务端,如果参数带有 “start-system-server” 调用 forkSystemServer 创建 SystemServer ,然后执行 runSelectLoop 开启 socket 监听
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
Runnable ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop(String abiList) {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> socketFDs = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<>();
socketFDs.add(mZygoteSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp = INVALID_TIMESTAMP;
while (true) {
fetchUsapPoolPolicyPropsWithMinInterval();
mUsapPoolRefillAction = UsapPoolRefillAction.NONE;
int[] usapPipeFDs = null;
StructPollfd[] pollFDs;
// Allocate enough space for the poll structs, taking into account
// the state of the USAP pool for this Zygote (could be a
// regular Zygote, a WebView Zygote, or an AppZygote).
if (mUsapPoolEnabled) {
usapPipeFDs = Zygote.getUsapPipeFDs();
pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size() + 1 + usapPipeFDs.length];
} else {
pollFDs = new StructPollfd[socketFDs.size()];
}
/*
* For reasons of correctness the USAP pool pipe and event FDs
* must be processed before the session and server sockets. This
* is to ensure that the USAP pool accounting information is
* accurate when handling other requests like API blacklist
* exemptions.
*/
int pollIndex = 0;
for (FileDescriptor socketFD : socketFDs) {
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = socketFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
final int usapPoolEventFDIndex = pollIndex;
if (mUsapPoolEnabled) {
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = mUsapPoolEventFD;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
// The usapPipeFDs array will always be filled in if the USAP Pool is enabled.
assert usapPipeFDs != null;
for (int usapPipeFD : usapPipeFDs) {
FileDescriptor managedFd = new FileDescriptor();
managedFd.setInt$(usapPipeFD);
pollFDs[pollIndex] = new StructPollfd();
pollFDs[pollIndex].fd = managedFd;
pollFDs[pollIndex].events = (short) POLLIN;
++pollIndex;
}
}
int pollTimeoutMs;
if (mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp == INVALID_TIMESTAMP) {
pollTimeoutMs = -1;
} else {
long elapsedTimeMs = System.currentTimeMillis() - mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp;
if (elapsedTimeMs >= mUsapPoolRefillDelayMs) {
// Normalize the poll timeout value when the time between one poll event and the
// next pushes us over the delay value. This prevents poll receiving a 0
// timeout value, which would result in it returning immediately.
pollTimeoutMs = -1;
} else if (elapsedTimeMs <= 0) {
// This can occur if the clock used by currentTimeMillis is reset, which is
// possible because it is not guaranteed to be monotonic. Because we can't tell
// how far back the clock was set the best way to recover is to simply re-start
// the respawn delay countdown.
pollTimeoutMs = mUsapPoolRefillDelayMs;
} else {
pollTimeoutMs = (int) (mUsapPoolRefillDelayMs - elapsedTimeMs);
}
}
int pollReturnValue;
try {
pollReturnValue = Os.poll(pollFDs, pollTimeoutMs);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
if (pollReturnValue == 0) {
// The poll timeout has been exceeded. This only occurs when we have finished the
// USAP pool refill delay period.
mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp = INVALID_TIMESTAMP;
mUsapPoolRefillAction = UsapPoolRefillAction.DELAYED;
} else {
boolean usapPoolFDRead = false;
while (--pollIndex >= 0) {
if ((pollFDs[pollIndex].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (pollIndex == 0) {
// Zygote server socket
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
socketFDs.add(newPeer.getFileDescriptor());
} else if (pollIndex < usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
// Session socket accepted from the Zygote server socket
try {
ZygoteConnection connection = peers.get(pollIndex);
final Runnable command = connection.processOneCommand(this);
// TODO (chriswailes): Is this extra check necessary?
if (mIsForkChild) {
// We're in the child. We should always have a command to run at
// this stage if processOneCommand hasn't called "exec".
if (command == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("command == null");
}
return command;
} else {
// We're in the server - we should never have any commands to run.
if (command != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("command != null");
}
// We don't know whether the remote side of the socket was closed or
// not until we attempt to read from it from processOneCommand. This
// shows up as a regular POLLIN event in our regular processing
// loop.
if (connection.isClosedByPeer()) {
connection.closeSocket();
peers.remove(pollIndex);
socketFDs.remove(pollIndex);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mIsForkChild) {
// We're in the server so any exception here is one that has taken
// place pre-fork while processing commands or reading / writing
// from the control socket. Make a loud noise about any such
// exceptions so that we know exactly what failed and why.
Slog.e(TAG, "Exception executing zygote command: ", e);
// Make sure the socket is closed so that the other end knows
// immediately that something has gone wrong and doesn't time out
// waiting for a response.
ZygoteConnection conn = peers.remove(pollIndex);
conn.closeSocket();
socketFDs.remove(pollIndex);
} else {
// We're in the child so any exception caught here has happened post
// fork and before we execute ActivityThread.main (or any other
// main() method). Log the details of the exception and bring down
// the process.
Log.e(TAG, "Caught post-fork exception in child process.", e);
throw e;
}
} finally {
// Reset the child flag, in the event that the child process is a child-
// zygote. The flag will not be consulted this loop pass after the
// Runnable is returned.
mIsForkChild = false;
}
} else {
// Either the USAP pool event FD or a USAP reporting pipe.
// If this is the event FD the payload will be the number of USAPs removed.
// If this is a reporting pipe FD the payload will be the PID of the USAP
// that was just specialized. The `continue` statements below ensure that
// the messagePayload will always be valid if we complete the try block
// without an exception.
long messagePayload;
try {
byte[] buffer = new byte[Zygote.USAP_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES];
int readBytes =
Os.read(pollFDs[pollIndex].fd, buffer, 0, buffer.length);
if (readBytes == Zygote.USAP_MANAGEMENT_MESSAGE_BYTES) {
DataInputStream inputStream =
new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(buffer));
messagePayload = inputStream.readLong();
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Incomplete read from USAP management FD of size "
+ readBytes);
continue;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (pollIndex == usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from USAP pool event FD: "
+ ex.getMessage());
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Failed to read from USAP reporting pipe: "
+ ex.getMessage());
}
continue;
}
if (pollIndex > usapPoolEventFDIndex) {
Zygote.removeUsapTableEntry((int) messagePayload);
}
usapPoolFDRead = true;
}
}
if (usapPoolFDRead) {
int usapPoolCount = Zygote.getUsapPoolCount();
if (usapPoolCount < mUsapPoolSizeMin) {
// Immediate refill
mUsapPoolRefillAction = UsapPoolRefillAction.IMMEDIATE;
} else if (mUsapPoolSizeMax - usapPoolCount >= mUsapPoolRefillThreshold) {
// Delayed refill
mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
if (mUsapPoolRefillAction != UsapPoolRefillAction.NONE) {
int[] sessionSocketRawFDs =
socketFDs.subList(1, socketFDs.size())
.stream()
.mapToInt(FileDescriptor::getInt$)
.toArray();
final boolean isPriorityRefill =
mUsapPoolRefillAction == UsapPoolRefillAction.IMMEDIATE;
final Runnable command =
fillUsapPool(sessionSocketRawFDs, isPriorityRefill);
if (command != null) {
return command;
} else if (isPriorityRefill) {
// Schedule a delayed refill to finish refilling the pool.
mUsapPoolRefillTriggerTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
}
总结:调用 acceptCommandPeer 获取到和客户端的 Socket 链接,调用 fillUsapPool 执行客户端发来的信息,也就是 fork 进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
Runnable ZygoteServer.fillUsapPool(int[] sessionSocketRawFDs, boolean isPriorityRefill) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Zygote:FillUsapPool");
// Ensure that the pool properties have been fetched.
fetchUsapPoolPolicyPropsIfUnfetched();
int usapPoolCount = Zygote.getUsapPoolCount();
int numUsapsToSpawn;
if (isPriorityRefill) {
// Refill to min
numUsapsToSpawn = mUsapPoolSizeMin - usapPoolCount;
Log.i("zygote",
"Priority USAP Pool refill. New USAPs: " + numUsapsToSpawn);
} else {
// Refill up to max
numUsapsToSpawn = mUsapPoolSizeMax - usapPoolCount;
Log.i("zygote",
"Delayed USAP Pool refill. New USAPs: " + numUsapsToSpawn);
}
// Disable some VM functionality and reset some system values
// before forking.
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
while (--numUsapsToSpawn >= 0) {
Runnable caller =
Zygote.forkUsap(mUsapPoolSocket, sessionSocketRawFDs, isPriorityRefill);
if (caller != null) {
return caller;
}
}
// Re-enable runtime services for the Zygote. Services for unspecialized app process
// are re-enabled in specializeAppProcess.
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
resetUsapRefillState();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
return null;
}
总结 :
调用 Zygote.forkUsap fork 进程
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
static Runnable Zygote.forkUsap(LocalServerSocket usapPoolSocket,
int[] sessionSocketRawFDs,
boolean isPriorityFork) {
FileDescriptor[] pipeFDs = null;
try {
pipeFDs = Os.pipe2(O_CLOEXEC);
} catch (ErrnoException errnoEx) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to create USAP pipe.", errnoEx);
}
int pid =
nativeForkUsap(pipeFDs[0].getInt$(), pipeFDs[1].getInt$(),
sessionSocketRawFDs, isPriorityFork);
if (pid == 0) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(pipeFDs[0]);
return usapMain(usapPoolSocket, pipeFDs[1]);
} else {
// The read-end of the pipe will be closed by the native code.
// See removeUsapTableEntry();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(pipeFDs[1]);
return null;
}
}
总结:
调用 nativeForkUsap 底层方法开启一个进程,然后调用 Zygote.usapMain 监听 Socket 发来的数据转换后设置新开启的进程
现在App的进程也创建成功了,就会进入 android.app.ActivityThread 的静态的main中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
// Install selective syscall interception
AndroidOs.install();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
// Call per-process mainline module initialization.
initializeMainlineModules();
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Find the value for {@link #PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT} if provided on the command line.
// It will be in the format "seq=114"
long startSeq = 0;
if (args != null) {
for (int i = args.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if (args[i] != null && args[i].startsWith(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT)) {
startSeq = Long.parseLong(
args[i].substring(PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT.length()));
}
}
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
Application 启动流程
当 ActivityThread.H 收到 BIND_APPLICATION 类型的消息时,就会调用 handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) 创建 Application
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data) {
// 创建 Application 对象,并调用 Application.attach 方法,attach 调用 Application.attachBaseContext(Context base)
app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
app.setAutofillOptions(data.autofillOptions);
app.setContentCaptureOptions(data.contentCaptureOptions);
mInitialApplication = app;
// 初始化 ContentProviders 对象,并调用 ContentProvider.onCreate 方法
if (!data.restrictedBackupMode) {
if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data.providers)) {
installContentProviders(app, data.providers);
}
}
// 调用 Application 的 onCtreate 方法
try {
mInstrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate(app);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
1. Click事件会调用startActivity(Intent), 会通过Binder IPC机制, 最终调用到ActivityManagerService. 该Service会执行如下操作:
- 第一步通过PackageManager的resolveIntent()收集这个intent对象的指向信息.
- 指向信息被存储在一个intent对象中.
- 下面重要的一步是通过grantUriPermissionLocked()方法来验证用户是否有足够的权限去调用该intent对象指向的Activity.
- 如果有权限, ActivityManagerService会检查并在新的task中启动目标activity.
- 现在, 是时候检查这个进程的ProcessRecord是否存在了.
- 如果ProcessRecord是null, ActivityManagerService会创建新的进程来实例化目标activity.
2. 创建进程
-
ActivityManagerService调用startProcessLocked()方法来创建新的进程, 该方法会通过前面讲到的socket通道传递参数给Zygote进程. Zygote孵化自身, 并调用ZygoteInit.main()方法来实例化 ActivityThread 对象并最终返回新进程的pid.
-
ActivityThread随后依次调用Looper.prepareLoop()和Looper.loop()来开启消息循环.
3. 绑定Application
- 接下来要做的就是将进程和指定的Application绑定起来. 这个是通过上节的ActivityThread对象中调用bindApplication()方法完成的. 该方法发送一个BIND_APPLICATION的消息到消息队列中, 最终通过handleBindApplication()方法处理该消息. 然后调用makeApplication()方法来加载App的classes到内存中.
4. 启动Activity
经过前两个步骤之后, 系统已经拥有了该application的进程. 后面的调用顺序就是普通的从一个已经存在的进程中启动一个新进程的activity了.
实际调用方法是realStartActivity(), 它会调用 application 线程对象中的sheduleLaunchActivity()发送一个LAUNCH_ACTIVITY消息到消息队列中, 通过 handleLaunchActivity()来处理该消息.
为什么 SystemServer(ASM) 进程与Zygote进程通讯采用Socket而不是Binder
为什么SystemServer进程与Zygote进程通讯采用Socket而不是Binder
Zygote.fork不允许存在多线程。而Binder 通讯是多线程,所以干脆父进程(Zgote)这个时候就不使用binder线程